ISO 8573-5 specifies a test method to determine the content of (gaseous) oil vapor in compressed air.
| Applying one of the test methods of ISO 8573-5 is mandatory for the allocation of a purity class according to ISO 8573-1. |
Most common is the partial flow method, i.e.
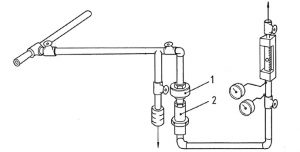
- for a defined time period a sample flow is taken from the turbulent compressed air main flow
- the sample flow is guided first to a high efficiency oil removal filter (1) and finally into the 2-zone activated carbon tube (2) (see Annex A)
- oil vapors are collected on the activated carbon
- at the end of the sampling period the collected oil is extracted from the activated carbon using a solvent, followed by a quantitative analysis using gas chromatography
- the determined oil mass is referred to the volume flow during the sampling period, resulting in the according mass concentration
The resulting measurement range of this method is stated as 0,001 mg/m³ to 10 mg/m³.
|
The ISO 8573-5 test method requires specialized technical competences and professional analytical skills and thus should be carried out by according specialized institutions. |
| Oil detector tubes are allowed for a preliminary test in order to decide for the required test period, typically applied with heavily contaminated compressed air. However, oil detector tubes cannot be used to align with any purity class. The method described in ISO 8573-5 shall be used to identify the (gaseous) oil contamination! (see Annex A.2) |
|
Within ambient air there may be higher oil vapor concentrations than those that can be measured in the compressed air. Thus any kind of contamination from the ambient air may result in a substantial measurement error. |
